Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid )
Long ago (1497), the British sailors on long voyages never reached their destinations because they got sick and some had painful deaths. James Lind, an English doctor, noticed that this strange disease (Scurvy) began after the supply of fresh fruits and vegetables ran out on the boat. As a way for trying to find a cure, he gave each sick sailor a daily drink of lime juice and they got better! This was because they lack vitamin C.
It’s a water-soluble vitamin (carry in the tissues but not stored in the body) They are found in food or dietary supplements and necessary to take daily.
Function
- Protective antioxidant helping to slow down/stop damage to cells thus, crucial for healthy cell metabolism. Protects against disease and protection against birth defects, increasing immunity.
Note: regular use of vitamin C may shorten the length of common cold, but does not prevent it neither used for treatment, this is according to World Health Organization (WHO)
- A perfect match with iron, the body absorbs iron more effectively with vitamin C, besides it helps synthesize RBC (iron is the main part of hemoglobin found in the RBC). This is important during pregnancy because the most common cause of true anemia is iron deficiency.
- May be prophylactic for postpartum hemorrhage
- Minimize risks of infection if rupture of membranes (ROM), which can occur if bacteria from the vagina enter the sterile uterine environment. Fluids intake makes her body defend itself by increasing the production of amniotic fluid, cleaning the vagina and avoiding bacteria from migrating upward.
Recommendation: take 250 mg of vitamin C every 4 hours, up to 2 g per day
Recommended Daily Intakes (RDIs)
Nonpregnant 60 mg
Pregnant 80 – 85mg/day
Lactating 115 – 120mg
Daily supplements 500mg
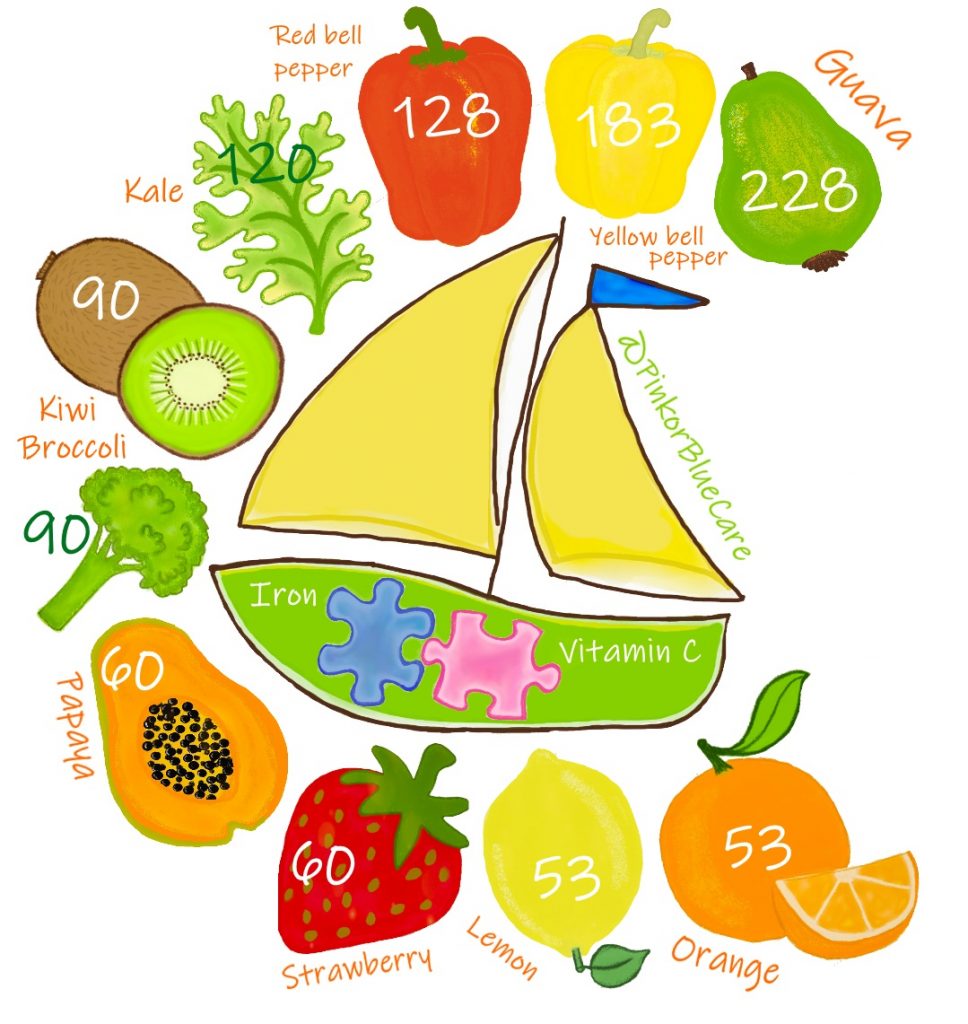
Sources of vitamin C per 100g
- Guava 228mg
- Yellow bell pepper 183mg
- Red bell pepper/capsicum 128mg
- Kale 120mg
- Kiwi / broccoli 90mg
- Papaya, strawberry 60mg
- Orange, lemon 53mg
- Pineapple, cauliflower 48mg
Deficiency
Scurvy
Due to a collagen synthesis defect.
Clinical manifestations: Swollen gums (gingivitis), bruising, anemia, poor wound healing, perifollicular and subperiosteal hemorrhages, “corkscrew” hair.
Weakened immune response.
Excess
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis.
- Can increase iron toxicity (Patients with hemochromatosis or transfusion-related iron overload)
- Can lead to a functional deficiency of vitamin B12 (Still controversial) consumption of vitamin B12 preconceptionally, same as folate, may decrease the risk of neural tube defects

excellent! Loved it.
Glad you like it! Hope you keep reading =)